GUIDELINES FOR AN INTEGRATED ENERGY STRATEGY
Helping companies achieve their sustainable energy objectives
Why does my company need an integrated energy strategy?
An integrated approach to energy will help companies to decrease and decarbonize their energy footprint and unlock value from the energy transition.
To respond to the climate change challenge, companies need not only decarbonize their own operations – they must also act to drive decarbonization into their supply chains and support their customer base to reduce their GHG emissions.
At the same time, energy users need to understand and respond to the energy systems becoming more decentralized, low-carbon and resilient. Most energy users aren’t just buying energy anymore, they’re now grappling with how to mitigate emerging risks, accelerate their transition to low-carbon operations and capture new commercial opportunities.
An integrated energy strategy will help your company navigate these challenges and capture a range of benefits.
To respond to climate change
The IPCC’s Special Report on ‘Global Warming of 1.5°C’ communicated a stark warning: avoiding the worst impacts of climate change requires “rapid, far-reaching and unprecedented changes in all aspects of society” and the complete decarbonization of the global economy. Today, around 80 percent of CO2 emissions come from the energy system. A radical transformation is required to transition the energy system away from its reliance on fossil fuels and towards zero carbon energy in all sectors.
An integrated energy strategy defines how your company responds to climate change and other environmental concerns: It helps you use less energy and transition towards net zero carbon energy.
To limit global warming to 1.5°C, GHG emissions need to be net zero as early as possible in the second half of this century and will need to be reduced by 45 percent by 2030 compared to 2010 levels. This time horizon is now within the business planning cycle of companies and requires companies to align their targets and actions. Failing to consider decarbonization in today’s business, and particularly investment decisions, increases the risk of disruption to business operations and reputational damage in the future.
As such, companies must consider decarbonization as a fundamental part of their integrated energy strategy.
To respond to an evolving energy system
An integrated energy strategy sets out how to achieve your company’s energy-related financial and environmental objectives by working cross-functionally internally and with upstream and downstream stakeholders externally. This means it assesses and clarifies the role your company plays in its evolving, interconnected, energy-related value chain. Failing to think and act strategically risks missing arising opportunities.
The traditional energy value chain was linear, with energy carriers produced centrally and distributed to a passive end user.
The traditional and linear energy value chain

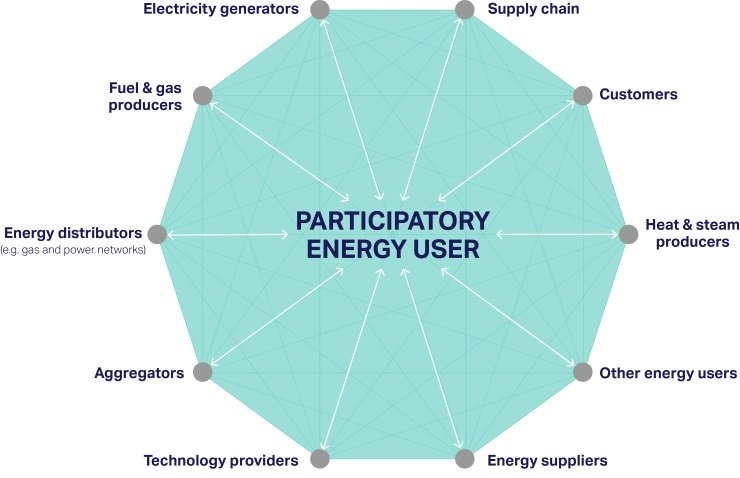
The emerging decentralized and interconnected energy value chain is characterized by distributed energy resources, technology-enabled collaboration, as well as new roles and business models. The energy user is a participatory player that can take multiple roles to suit their business model.
Companies who take advantage of the energy system transformation evaluate what energy inputs they really need, where those are available and how their products, services and by-products/waste streams can provide low-carbon energy solutions to other energy consumers. They will have a comprehensive understanding of their energy consumption and leverage the demand side and supply side with a collaborative approach. They will look to recover and extract value from energy resources that would otherwise go to waste and consider local partnerships to share energy resources efficiently.
Companies who understand how they fit within the interconnected energy value chain and where their opportunities lie will benefit most from the transition.
Traditional energy value chain and passive energy user
- Limited sources of fuel production and electricity generation
- Limited choice of suppliers
- Limited capabilities in switching to more efficient and low-carbon technologies
Evolving energy system and active energy user
- Energy users’ interest in energy management drives new choices
- Broader choice of suppliers, products and services lead to an active selection of suppliers that will help to achieve strategic objectives
- Energy user doesn’t control fuel production or electricity generation, but has stronger influence via sourcing choices
- Energy efficient technologies
Decentralized & interconnected energy value chain and participatory energy user
- Energy user takes a participatory role in fuel production, electricity generation, storage and management
- Comprehensive understanding of the technologies can improve energy and fuel efficiency, while reducing GHG emissions
- Increasing interactions with other players across the energy value chain
- Involvement in energy recovery and reuse solutions
- Creation of new energy supply options for property, plants and transport fleets
To collaborate with upstream and downstream stakeholders
An integrated energy strategy enables a company to collaborate with stakeholders that sit outside its traditional energy value chain. It harnesses knowledge, expertise and relationships that exist with an organization’s suppliers and customers to find more energy efficient, circular and low-carbon ways of doing business.
When companies become actively engaged with their supply chain and customers on the topic of energy resources, they can create advantages by developing new capabilities, exploring new business models, capturing new revenue streams and finding energy and cost efficiencies.
When procuring products or services that have an impact on your company’s energy use or GHG emissions, there’s an opportunity to work with upstream stakeholders to improve energy efficiency and lower the carbon content of purchased goods and services. Similarly, companies can engage with their customers to ensure they understand how their products and services can help them reduce their carbon impacts. This might lead to further collaboration and help their customers to lower GHG emissions.
Companies may also benefit from collaborating with companies in their vicinity. Using the concept of industrial symbiosis, companies may find that their by-products/waste is another company’s input, potentially reducing operating costs, securing financial gains or mitigating risk. Steam, sludge, biomass and other by-products of primary production processes can generate value for companies who identify the right partners.
The benefits of an integrated energy strategy
FINANCIAL
- Manage energy and maintenance costs
- Reduce costs associated with carbon pricing
- Explore new revenue streams and commercial models
- Improve business performance and productivity
- Extend asset life
RISK
- Improve security of supply
- Reduce exposure to energy price volatility
- Improve resilience against policy and legal risks
- Reduce exposure to stranded assets
- Reduce reputational risk
INNOVATION
- Innovation with suppliers provides a competitive advantage
- Innovation with customers builds loyalty
- Innovation with local end users enables new technologies, commercial and financing solutions
ENVIRONMENTAL
- Reduce life-cycle GHG emissions in alignment with SDG 13 and the Paris Agreement
- Reduce life-cycle air quality and water quality impacts in alignment with SDG 3
- Reduce life-cycle biodiversity impacts in alignment with SDG 15
- Reduce waste and improve circularity in alignment with SDG 12
SOCIO-ECONOMIC
- Contribute to job creation and reduce economic inequality in alignment with SDG 8
- Improve labor practices and human rights in your supply chain in alignment with SDG 8
- Provide access to new sources of clean energy for local communities in alignment with SDG 7
LEADERSHIP
- Build brand reputation and improve performance in sustainability benchmarking
- Improveinvestor confidence and attract investment from new sources
- Improve talent acquisition and retention

Copyright © 2025
World Business Council for Sustainable Development
All rights reserved | Privacy Policy